Cpu Core Temperature Vs Socket Temperature – A Complete Guide!
CPU core temperature measures heat from the CPU cores, while socket temperature gauges heat around the socket. Monitoring both prevents overheating.
In this article, we’ll explore what these temperatures mean, why they matter, and how you can monitor and manage them.
Table of Contents
What is CPU Core Temperature?
The CPU core temperature refers to the temperature of the individual processing units, or cores, within the central processing unit (CPU). Modern CPUs have multiple cores, and each of these cores generates heat while performing tasks. The core temperature tells you how hot each of these cores is during operation.
Why CPU Core Temperature is Important:
The CPU core temperature is important because it affects the performance and longevity of your CPU. If the cores run too hot, they can become damaged over time or cause the CPU to throttle its performance to prevent overheating.
Overheating can lead to sudden shutdowns, slower performance, or even permanent hardware damage.Monitoring the core temperature helps ensure that the CPU is operating within safe limits, which can prolong its life and maintain optimal performance.
What is a Safe CPU Core Temperature?
Safe CPU core temperatures vary depending on the CPU model, but generally, it is best to keep the temperature below 80°C (176°F) under heavy load. Idle temperatures should ideally range between 30°C and 50°C (86°F to 122°F). If your CPU constantly runs above these levels, it’s a sign that your cooling system may not be sufficient.
What is Socket Temperature?
Socket temperature refers to the temperature of the CPU’s socket on the motherboard, where the CPU is physically mounted. This is the temperature measured by a sensor placed near the CPU socket, which indicates how hot the surrounding area of the motherboard is.
While socket temperature is related to the overall heat produced by the CPU, it doesn’t give a direct reading of the core temperatures. Instead, it measures the heat surrounding the CPU, which can also affect other components like RAM and power regulators.
Why Socket Temperature is Important:
Socket temperature is crucial because high temperatures in this area can affect more than just the CPU. Other parts of the motherboard, such as voltage regulators and capacitors, can be impacted by excessive heat, leading to instability and reduced lifespan of the components.
By monitoring the socket temperature, users can ensure that their motherboard stays cool and that no other parts are overheating due to poor airflow or insufficient cooling.
What is a Safe Socket Temperature?
A safe socket temperature generally ranges from 40°C to 70°C (104°F to 158°F). If the socket temperature exceeds these limits, it may indicate poor airflow, insufficient cooling, or issues with thermal paste or heatsinks.
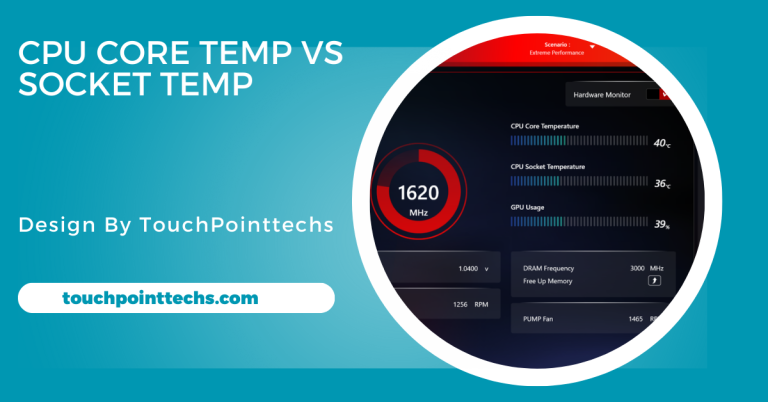
CPU Core Temperature vs Socket Temperature – Key Differences:
Now that we’ve defined CPU core temperature and socket temperature, let’s compare the two to understand their differences.
Source of Measurement:
- CPU Core Temperature: Directly measures the heat generated by the CPU cores during operation.
- Socket Temperature: Measures the heat around the CPU socket, giving an indirect reading of the overall temperature around the CPU.
Impact on Performance:
- Core Temperature: High core temperatures can directly affect the CPU’s performance, leading to throttling (reducing the CPU’s speed to prevent overheating) or even shutdowns.
- Socket Temperature: While it doesn’t directly affect CPU performance, high socket temperatures can impact the motherboard’s components and lead to system instability or hardware damage.
Monitoring Accuracy:
- Core Temperature: Core temperatures tend to fluctuate more rapidly, especially under load, and are a more accurate reflection of the CPU’s internal heat.
- Socket Temperature: Socket temperatures are generally more stable but may not accurately reflect the actual heat of the CPU cores.
Safe Temperature Ranges:
- Core Temperature: Ideal under load: below 80°C (176°F).
- Socket Temperature: Ideal: below 70°C (158°F).
How to Monitor CPU Core and Socket Temperatures:
To effectively monitor CPU core and socket temperatures, you can utilize a variety of software tools:
- Core Temp: This lightweight tool monitors each CPU core’s temperature in real-time. It’s user-friendly and offers accurate readings, making it ideal for quick checks.
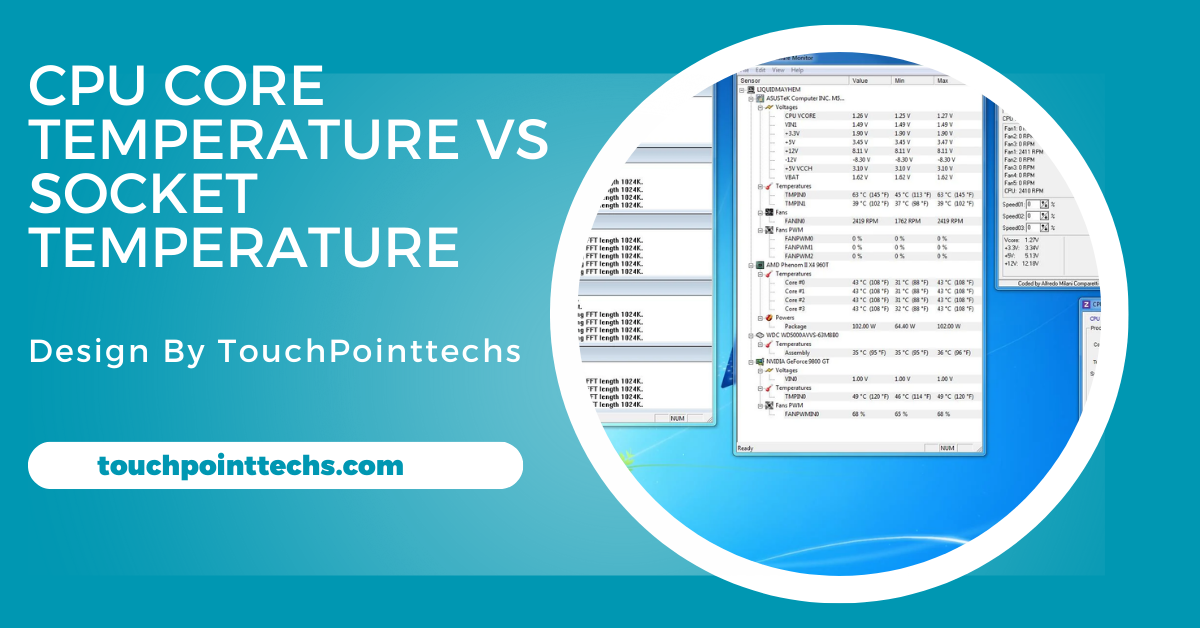
- HWMonitor: A comprehensive tool that provides detailed temperature readings for various components, including both CPU core and socket temperatures. It’s excellent for monitoring the overall health of your computer hardware.
- SpeedFan: This versatile tool not only tracks core and socket temperatures but also allows you to control the speed of your system’s fans. By adjusting fan speeds, you can improve cooling and reduce heat buildup.
- AIDA64: A more advanced option, AIDA64 offers in-depth diagnostics, including precise monitoring of both CPU core and socket temperatures. It also provides additional information on other hardware components.
By using these tools, you can keep a close eye on your CPU’s temperature, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating.
How to Manage High CPU Core and Socket Temperatures
If you notice that your CPU core or socket temperatures are consistently high, it’s essential to take steps to manage and reduce them. High temperatures can lead to performance issues, instability, and even permanent damage to your components.
- Improve Airflow in Your Case:One of the easiest ways to reduce CPU temperatures is to improve airflow inside your computer case. This can be done by adding more fans or rearranging your existing fans to create better airflow.
- Upgrade Your CPU Cooler: If improving airflow doesn’t solve the issue, you may need to upgrade your CPU cooler. Stock coolers that come with CPUs are often not sufficient for keeping temperatures down, especially under heavy load.
- Apply New Thermal Paste: Thermal paste helps conduct heat between the CPU and the cooler. Over time, this paste can dry out, reducing its effectiveness. Reapplying high-quality thermal paste can help improve heat transfer and lower CPU temperatures.
- Reduce CPU Load: High CPU loads cause the CPU cores to heat up quickly. To prevent overheating, consider reducing the load on your CPU by closing unnecessary applications or adjusting the settings in resource-intensive programs like games or video editing software.
- Use a Fan Control Software: Fan control software, like SpeedFan, allows you to manually adjust the speed of your computer’s fans to increase airflow and cooling. Increasing the fan speed can help lower both core and socket temperatures, especially during demanding tasks.
The Importance of Maintaining Safe Temperatures:
Both CPU core and socket temperatures play a significant role in your system’s performance and longevity. Keeping these temperatures within safe limits ensures that your computer runs smoothly without overheating or damaging components.
Avoiding Throttling and Shutdowns:
High CPU core temperatures can lead to throttling, where the CPU reduces its speed to prevent overheating. In extreme cases, the CPU may shut down entirely to protect itself from damage. Keeping core temperatures in check ensures that your CPU runs at full speed without interruptions.
Protecting Your Motherboard:
High socket temperatures can cause overheating in other components of the motherboard, such as voltage regulators and capacitors. By monitoring socket temperatures, you can prevent damage to these critical components and avoid costly repairs or replacements.
FAQ’s
1. What is the difference between CPU core temperature and socket temperature?
CPU core temperature measures the heat of individual cores, while socket temperature gauges the heat around the CPU’s mounting area on the motherboard.
2. Why is monitoring CPU core temperature important?
Monitoring core temperature is crucial to prevent overheating, which can cause performance throttling, shutdowns, or permanent hardware damage.
3. What is a safe CPU core temperature range?
A safe core temperature range is typically below 80°C under load and between 30°C-50°C when idle.
4. Why should I monitor socket temperature?
Monitoring socket temperature helps prevent damage to other components on the motherboard, such as voltage regulators, ensuring system stability.
5. How can I reduce high CPU core and socket temperatures?
You can reduce temperatures by improving airflow, upgrading the CPU cooler, applying fresh thermal paste, and managing CPU load.
Conclusion
In conclusion, monitoring both CPU core and socket temperatures is vital for maintaining optimal computer performance. Understanding their differences helps prevent overheating, ensuring the longevity of the CPU and motherboard. Effective cooling strategies protect against throttling and potential damage.