How To Read Cpu Names – A Simple Guide To Understanding Processors!
Reading CPU names is crucial for understanding a processor’s capabilities, generation, and features. By decoding naming conventions, you can select the right CPU for your computing needs.
In this article, we will explain how to read CPU names, what the different parts mean, and how to choose the right one for you.
Table of Contents
What Is a CPU?
A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the main component of a computer, often called its “brain.” It performs the majority of processing tasks by executing instructions from programs and managing data. The CPU coordinates the activities of other hardware components, making its performance crucial for the speed and efficiency of the computer, affecting everything from simple tasks to complex applications.
Why Is It Important to Read CPU Names?
Reading CPU names is vital for making informed decisions when purchasing or upgrading computers. The names provide essential information about a processor’s capabilities, generation, and features. Understanding these details helps you compare different CPUs effectively and choose one that fits your needs, whether for gaming, multitasking, or specific applications, ensuring you get the best performance for your computing tasks.
What Are CPU Naming Conventions?
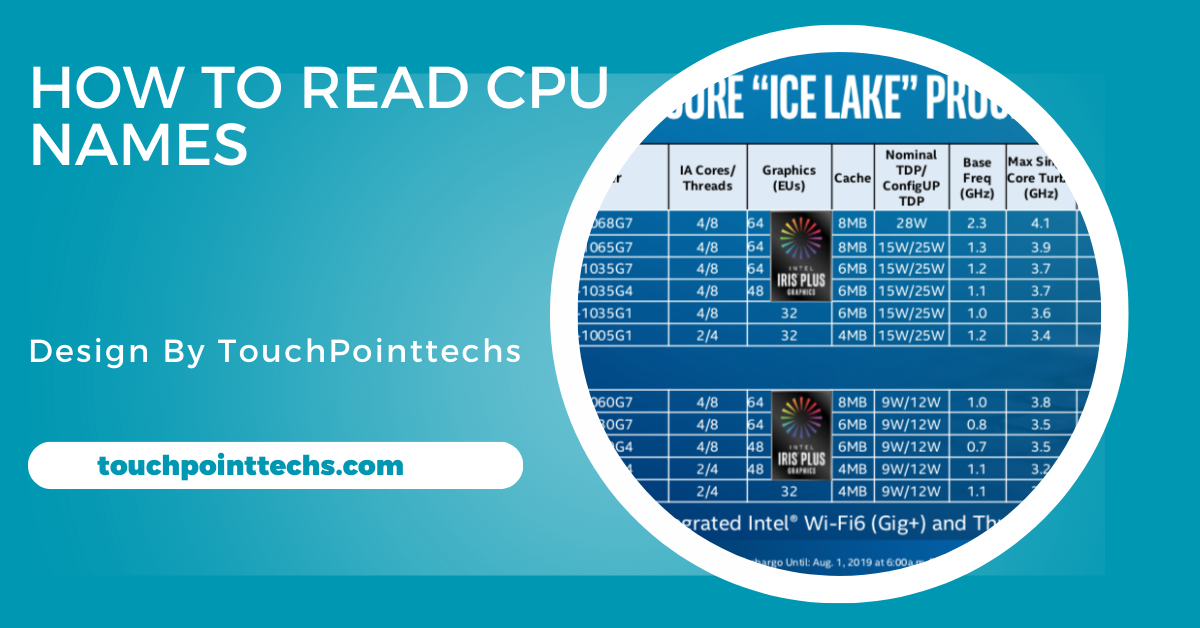
CPU naming conventions are the systematic ways manufacturers label their processors to convey essential information about performance, features, and generation. These names often include details like the model, series, and sometimes specific functionalities, allowing consumers to understand the capabilities of a CPU at a glance. Understanding these conventions is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Key Components of CPU Names:
CPU names typically consist of several parts, each providing different insights. The first part often indicates the brand (like Intel or AMD), followed by a series number that signifies the generation. Additional suffixes may denote specific features, such as enhanced performance or power efficiency. By deciphering these components, you can better assess which processor meets your needs.
Importance of Knowing CPU Naming Conventions:
Understanding CPU naming conventions allows consumers to compare different processors effectively and choose the right one for their needs. It helps identify the most suitable options for various tasks, such as gaming, content creation, or general use. Moreover, it can aid in future-proofing your purchase, ensuring that you select a CPU that will remain relevant as software demands evolve.
Comparing Intel and AMD Processors:
Performance:
When choosing between Intel and AMD processors, performance is a key factor. Intel CPUs often excel in single-threaded tasks, making them ideal for gaming and applications that rely on high clock speeds. On the other hand, AMD processors generally provide better multi-threaded performance, which is beneficial for tasks like video editing and rendering. Your specific needs will influence which brand you prefer.
Price:
Price is another crucial consideration when selecting between Intel and AMD. AMD processors are frequently recognized for their cost-effectiveness, offering solid performance at more affordable price points. In contrast, Intel CPUs, particularly at the higher end, can be pricier. However, prices can vary widely among specific models, so it’s important to compare the options available within your budget to ensure you get the best value.
Compatibility:
Compatibility plays a vital role in your processor choice. Intel and AMD processors require different types of motherboards, meaning you cannot interchange them. Ensure that your motherboard supports the CPU you select to avoid any issues. Check the socket type and chipset compatibility before making a purchase to guarantee a seamless installation and optimal performance from your new processor.
How to Choose the Right CPU for Your Needs:
Your Usage Needs:
Begin by evaluating your primary usage needs. For basic tasks like web browsing and document editing, a lower-end CPU such as an Intel Core i3 or AMD Ryzen 3 will suffice. However, if your activities include gaming, video editing, or running demanding software, consider investing in a more powerful processor like a Core i7 or Ryzen 7 for optimal performance.
Budget:
Establish a clear budget for your CPU purchase to guide your decision. While high-end processors deliver impressive performance, they often come with a hefty price tag. Assess how much you are willing to spend and search for CPUs that fit within your financial limits, ensuring you get the best possible value without overspending.
Future Upgrades:
Think about your future upgrade plans when selecting a CPU. If you anticipate upgrading other components down the line, it might be wise to invest in a slightly better CPU now. A more powerful processor will provide longevity and compatibility with emerging technologies, making it easier to upgrade without needing to replace the CPU again soon.
Research:
Dedicate time to researching specific CPU models before making a purchase. Review websites and online forums can provide valuable benchmarks and user reviews, offering insight into how each CPU performs in real-world situations. By gathering this information, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your requirements and expectations.
Tools to Help You Read CPU Names:
Several online tools can help you decode CPU names and understand their specifications. Some popular websites include:
- CPU Benchmark: Provides detailed benchmarks and comparisons of various processors.
- PassMark Software: Offers CPU ratings based on performance testing.
- UserBenchmark: Allows users to compare CPU performance based on real-world usage.
Using these tools can simplify the process of reading CPU names and help you make informed decisions.
FAQ’s
1. What does CPU stand for?
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit, which is the main part of a computer that handles processing tasks. It is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer.
2. Why is it important to read CPU names?
Reading CPU names helps you understand a processor’s capabilities and features. This knowledge ensures you choose the right CPU for gaming, multitasking, or specific applications.
3. What do the numbers in CPU names represent?
The numbers typically indicate the brand, series, generation, and specific model of the processor. They provide important insights into its performance and capabilities.
4. How do Intel and AMD CPU names differ?
Intel uses names like Core i3, i5, i7, and i9, while AMD uses Ryzen 3, 5, 7, and 9. Each brand’s naming convention helps indicate performance and generation.
5. How can I choose the right CPU for my needs?
To choose the right CPU, assess your usage needs and set a budget. Also, consider future upgrades and research specific models to find the best fit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how to read CPU names is essential for making informed choices when purchasing or upgrading your computer. By familiarizing yourself with CPU naming conventions and key components, you can evaluate processors based on your needs, performance requirements, and budget. With the right knowledge, you can ensure that you select a CPU that will provide optimal performance for your tasks, whether for gaming, content creation, or everyday use.