Antimalware Service Executable High Cpu – A Complete Guide!
Antimalware Service Executable uses a high CPU for scanning, real-time protection, and full scans. Updating Windows and scheduling scans can reduce CPU usage.
This guide will help you understand why this happens and how to fix it.
Table of Contents
What Is Antimalware Service Executable?
Definition of Antimalware Service Executable:
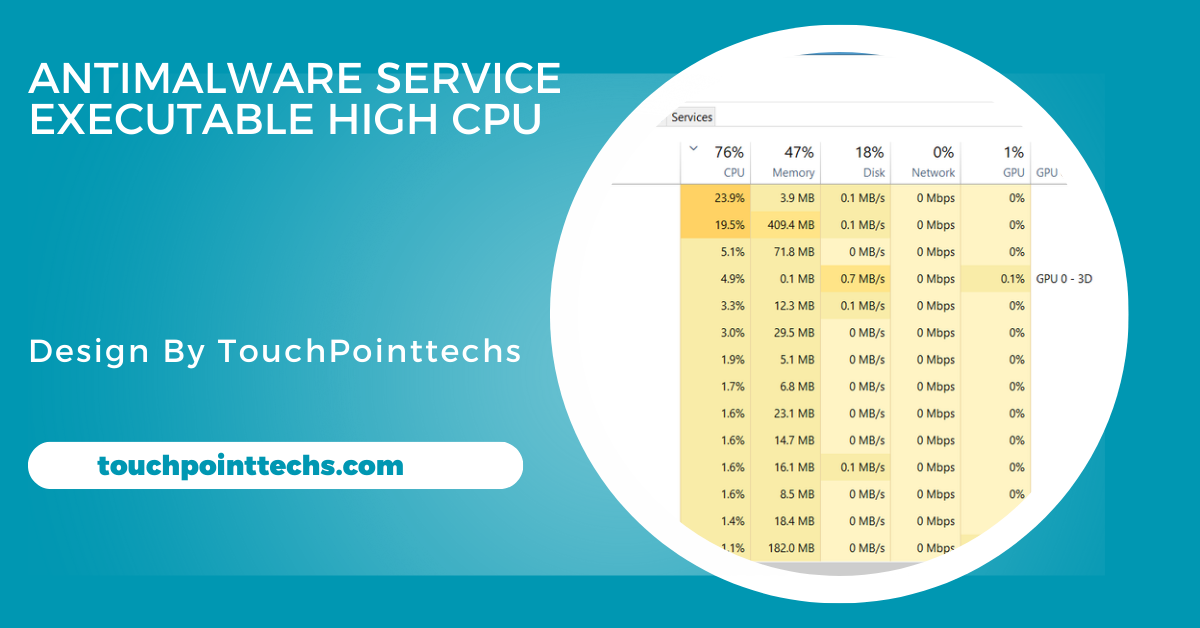
Antimalware Service Executable is a built-in process in Windows responsible for running Microsoft Defender. It scans files, programs, and applications on your computer to protect against malware. In the Task Manager, it appears as MsMpEng.exe. This essential feature ensures your system remains secure by actively identifying and removing malicious threats before they can cause harm to your computer.
Why Is It Important?
Antimalware Service Executable is crucial for safeguarding your system. It offers real-time protection by continuously monitoring your computer for malware, viruses, and other cyber threats. By detecting and neutralizing these risks, it keeps your system safe and your data secure. Without this process, your computer would be far more exposed to potential attacks, jeopardizing its performance and your personal information.
Why Does Antimalware Service Executable Use High CPU?
Scanning Files and Programs:
Antimalware Service Executable scans files and programs to detect potential threats. This scanning process can consume a lot of CPU resources, especially when it’s scanning large or numerous files. As the service checks for malware or viruses, the system’s performance might temporarily slow down due to the high CPU usage, especially during deeper scans or when scanning programs that are running in the background.
Real-Time Protection:
The real-time protection feature of Antimalware Service Executable constantly monitors the system for suspicious activities. This includes scanning incoming files and programs as you download or run them. The continuous monitoring can occasionally lead to higher CPU usage, especially when performing resource-intensive tasks or applications. It ensures your computer is always protected but can cause a slowdown during heavy system usage.
Full Scans During Active Hours:
At times, Windows Defender runs full system scans, which can happen during your active hours. When this occurs, the Antimalware Service Executable uses substantial CPU power to thoroughly check the entire system for malware. This can cause noticeable slowdowns, especially when you are actively using the computer for tasks like gaming, working, or browsing. Full scans are vital but can interfere with performance.
Outdated System or Software:
If Windows or Microsoft Defender is outdated, the Antimalware Service Executable may not work efficiently, leading to higher-than-normal CPU usage. Updates are crucial for improving the performance and functionality of the service. Without the latest system updates or Defender updates, it may struggle to complete tasks, causing slower scans, inefficient threat detection, and, ultimately, more resource consumption, which slows down the system.
How to Fix Antimalware Service Executable High CPU?
Update Windows and Defender:
Updating ensures the service runs smoothly and fixes any bugs that might cause high CPU usage.
Steps to Update Windows:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security.
- Click Check for updates.
- Install any available updates.
Steps to Update Defender:
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & threat protection.
- Click Check for updates under Virus & threat protection updates.
Schedule Scans for Idle Times:
You can set scans to run during times when you’re not using the computer.
Steps to Schedule Scans:
- Open the Task Scheduler.
- Navigate to Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender.
- Right-click Windows Defender Scheduled Scan and select Properties.
- Set a time when you’re not using the computer.
Exclude Defender from Scanning Itself:
Sometimes, Defender scans its own files, causing high CPU usage. Excluding these files can help.
Steps to Exclude Defender Files:
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & threat protection > Manage settings.
- Scroll to Exclusions and click Add or remove exclusions.
- Add the path:
C:\Program Files\Windows Defender.
Disable Real-Time Protection (Temporarily):
Turning off real-time protection can reduce CPU usage, but this should only be temporary for safety reasons.
Steps to Disable Real-Time Protection:
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & threat protection > Manage settings.
- Toggle off Real-time protection.
Use Third-Party Antivirus Software:
If Windows Defender is consistently using a high CPU, you might consider switching to third-party antivirus software like Avast, Norton, or Kaspersky. These alternatives offer strong protection against malware and viruses, while often using fewer system resources. By opting for a third-party solution, you can reduce CPU usage without sacrificing the security of your system, allowing for better overall performance without compromising your protection.
Preventing High CPU Usage in the Future:
Schedule Scans at Convenient Times:
To avoid disrupting your activities, schedule full system scans during off-peak hours, such as late at night. By adjusting the scan schedule in Windows Security settings, you can ensure Windows Defender runs without affecting your daily tasks. This way, scans happen when you’re not using the system, optimizing CPU resources and preventing slowdowns during important activities like gaming or work.
Keep Your System Updated:
Regularly updating both Windows and Windows Defender ensures smooth performance and minimizes bugs that could cause high CPU usage. Keeping your software up to date also improves security by patching vulnerabilities, preventing potential performance issues, and optimizing system resource usage. Check for updates frequently to avoid CPU strain from outdated software, ensuring Windows Defender runs efficiently without negatively affecting your computer’s performance.
Optimize System Resources:
Reduce CPU usage by disabling unnecessary background programs and managing startup items. Access Task Manager to identify apps that use excessive resources and disable them from running at startup. By minimizing background processes, you free up system resources for other important tasks, ensuring that Windows Defender can run without consuming too much CPU power. This leads to smoother performance overall.
Use Efficient Antivirus Software:
If Windows Defender consistently uses too much CPU, consider switching to third-party antivirus software. Programs like Avast, Norton, and Kaspersky are alternatives that provide similar protection but may be more resource-efficient. Research these options based on performance and CPU consumption, and choose one that delivers security without causing lag or slowdowns. This ensures efficient protection while keeping CPU usage low during scans.
FAQ’s
1. What is Antimalware Service Executable?
It is a process in Windows that runs Microsoft Defender to protect your system from malware and viruses.
2. Why is it using a high CPU?
It uses high CPU during file scans, real-time protection, or full system scans, especially when running in the background.
3. How can I reduce high CPU usage from this process?
Update Windows and Defender, schedule scans during idle times, and exclude Defender from scanning its own files.
4. Is it safe to disable real-time protection?
Disabling real-time protection can reduce CPU usage temporarily, but it leaves your system vulnerable to threats, so it should only be a temporary solution.
5. Can I use third-party antivirus software instead?
Yes, you can use third-party antivirus software like Avast or Norton to reduce CPU usage while still keeping your system secure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Antimalware Service Executable may cause high CPU usage due to its scanning and real-time protection. To minimize strain, schedule scans during idle times and keep your system updated. If the issue persists, consider using third-party antivirus software to maintain security while optimizing system performance, ensuring your computer stays protected without causing excessive CPU usage.