Cpu Overheating – Causes, Symptoms, And How To Fix It!
CPU overheating happens when the processor exceeds safe temperatures, causing slowdowns, crashes, and shutdowns. Prevent it with proper airflow, cleaning, and temperature monitoring.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and solutions for CPU overheating.
Table of Contents
What is CPU Overheating?
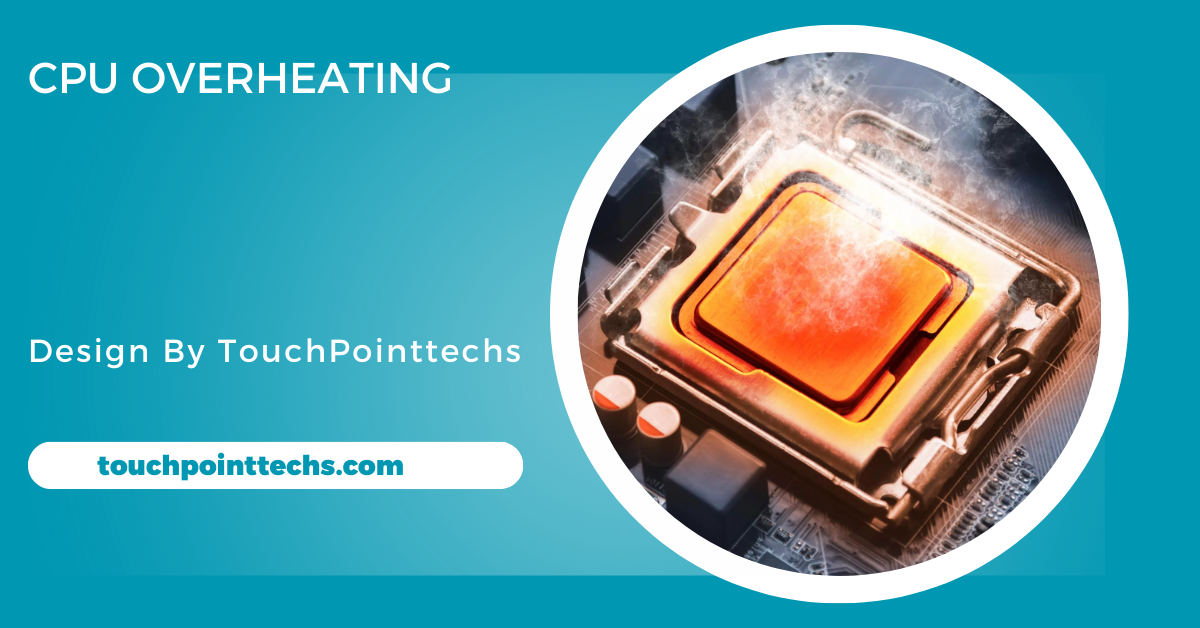
CPU overheating happens when the Central Processing Unit exceeds its safe temperature range, causing performance issues. The CPU performs essential tasks, and when it gets too hot, it can lead to slowdowns, system freezes, or even shutdowns. Overheating may result in thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces speed to prevent damage, or permanent damage, negatively impacting system performance and potentially shortening the lifespan of the CPU if not addressed promptly.
Ideal CPU Temperature Range:
The ideal temperature range for most CPUs is between 40°C (104°F) and 70°C (158°F). High-performance CPUs, such as those in gaming or video editing systems, may run safely at temperatures up to 90°C (194°F). However, temperatures exceeding this limit can cause thermal throttling, which reduces performance, or even permanent damage to the CPU. Ensuring proper cooling and maintaining temperatures within these ranges is essential for optimal CPU performance and longevity.
Causes of CPU Overheating:
Understanding the causes of CPU overheating is the first step in preventing it. There are several factors that can contribute to an overheating CPU:
Poor Airflow in the Computer Case:
Poor airflow inside the computer case can cause the CPU to overheat as the cooling system relies on efficient airflow. Dust, clutter, or poor design can block vents and restrict air circulation. As a result, the heat generated by the CPU and other components cannot escape, causing the CPU temperature to rise. To prevent this, keep the case clean, ensure there is enough space for airflow, and optimize internal cooling components to improve temperature regulation and prevent overheating.
Dust and Debris Buildup:
Dust and debris can accumulate inside your computer case over time, clogging fans, heatsinks, and vents. This obstructs airflow and reduces the effectiveness of your cooling system. When cooling components are clogged, the CPU fails to dissipate heat properly, leading to overheating. To combat this, regularly clean the interior of your case using compressed air. Removing dust and ensuring unobstructed airflow helps keep the CPU cool, reducing the risk of overheating and improving system performance.
Malfunctioning CPU Cooler:
A malfunctioning CPU cooler, whether a fan or heatsink, can’t properly dissipate the heat generated by the CPU. If the cooler is damaged, clogged, or improperly installed, it can result in higher CPU temperatures and overheating. A malfunctioning cooler can strain the CPU and lead to thermal throttling or permanent damage. To avoid this, regularly check that the cooler is working correctly and replace or clean it if necessary to ensure effective cooling and prevent overheating.
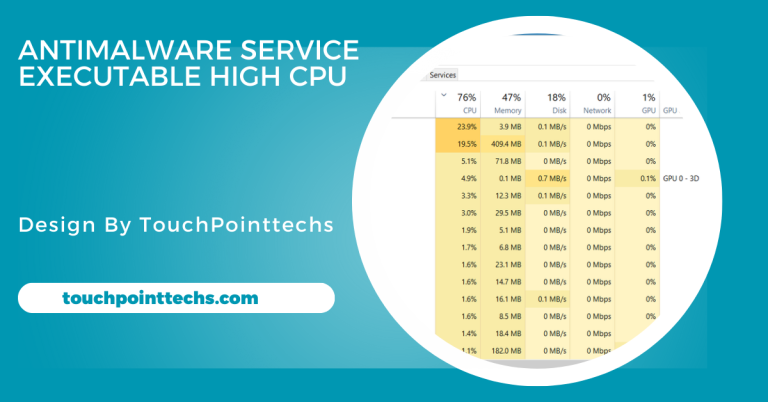
High CPU Usage:
High CPU usage occurs when resource-intensive programs, like games or video editing software, push the processor to its limits. Prolonged heavy usage generates excess heat, which may overwhelm the cooling system, leading to overheating. This is especially true when multiple applications are running simultaneously. To prevent overheating, monitor CPU performance with task managers, close unnecessary programs, and ensure your cooling system can handle high workloads. Proper cooling and task management help maintain safe CPU temperatures.
Overclocking:
Overclocking increases the CPU’s clock speed for better performance, but it also results in more heat generation. If the cooling system isn’t upgraded to handle this extra heat, the CPU can overheat. Overclocking forces the processor to run beyond its default settings, causing higher temperatures and potential damage over time. To avoid overheating, ensure your cooling system is adequate for overclocking. Also, monitor CPU temperatures closely to ensure the system remains stable and avoid thermal damage.
Thermal Paste Issues:
Thermal paste is crucial for transferring heat from the CPU to the cooler or heatsink. If the thermal paste is old, dry, or improperly applied, it reduces the heat transfer efficiency, causing the CPU to overheat. This results in higher CPU temperatures and can negatively affect performance. To prevent this, check the thermal paste regularly and reapply it when needed. Fresh, properly applied thermal paste ensures better heat dissipation, helping maintain safe CPU temperatures and preventing overheating.
Ambient Temperature:
The temperature of the room where your computer is located can directly impact CPU cooling. If the ambient temperature is too high, the cooling system may struggle to dissipate heat effectively, leading to overheating. Even with adequate internal cooling, a hot room can prevent the CPU from maintaining safe operating temperatures. To avoid this, place the computer in a cool, well-ventilated area where the air entering the case remains cool enough to prevent overheating.
Symptoms of CPU Overheating:
Recognizing the symptoms of CPU overheating is important for preventing damage to your computer. Some common signs that your CPU may be overheating include:
Slow Performance:
When the CPU overheats, it may throttle its performance to reduce heat, leading to slower processing speeds. You might notice delays when opening files, running programs, or performing simple tasks. The computer may struggle to keep up with regular functions, which impacts overall user experience. If you observe significant lag or slowdowns, it could indicate that the CPU is getting too hot and requires attention, such as improving cooling or reducing heavy workload.
Frequent Shutdowns or Restarts:
To protect itself from potential damage, the CPU may cause your computer to shut down automatically when temperatures become dangerously high. In some instances, your system might restart repeatedly, unable to stabilize due to overheating. Frequent unexpected shutdowns or restarts are clear symptoms of CPU overheating. This protective mechanism prevents permanent damage, but it’s essential to address the underlying cooling issues to avoid system instability and potential hardware failure.
Freezing or Crashing:
Overheating can cause programs or applications to freeze, crash, or close unexpectedly. This is often due to the CPU being unable to handle its workload when it’s too hot. If your computer frequently freezes or crashes without warning, it may be a sign of excessive heat. Regular freezing or unexpected terminations of programs are indications that the CPU is overheating and that cooling solutions need to be checked or improved for proper functioning.
Loud Noises from the Fans:
If your computer’s cooling system struggles to maintain the CPU temperature, the fans may start spinning faster and louder than usual. This is a sign that the system is under stress, working harder to cool the CPU. Loud fan noises are typically heard when the CPU temperature rises significantly, triggering the cooling system into overdrive. If this happens frequently, it could indicate overheating, requiring cleaning or upgrading of cooling components to avoid damage.
Error Messages or Blue Screens:
In extreme cases, CPU overheating can trigger error messages or lead to a blue screen of death (BSOD). These errors occur when the CPU fails to maintain stable performance due to high temperatures, causing the system to shut down unexpectedly. The blue screen is a protective mechanism that prevents further damage. If you encounter frequent BSODs or error messages, it’s crucial to check the CPU temperature and improve cooling to prevent hardware failure.
Preventing Future Overheating:
To avoid CPU overheating in the future, here are some preventive measures you can take:
- Regularly clean your computer to prevent dust buildup.
- Monitor CPU temperature using software tools.
- Replace thermal paste every few years.
- Ensure your computer is placed in a cool and ventilated area.
- Upgrade your cooling system if necessary.
FAQ’S
1. What causes CPU overheating?
CPU overheating can be caused by poor airflow, dust buildup, a malfunctioning cooler, high CPU usage, overclocking, thermal paste issues, or high ambient temperatures.
2. How can I tell if my CPU is overheating?
Common signs of CPU overheating include slow performance, frequent shutdowns or restarts, freezing, loud fan noises, and error messages or blue screens.
3. What is the ideal temperature for a CPU?
The ideal temperature range for most CPUs is between 40°C (104°F) and 70°C (158°F). Temperatures exceeding 90°C (194°F) can cause performance issues or damage.
4. How can I fix a CPU that’s overheating?
To fix overheating, improve airflow in the case, clean out dust, check the CPU cooler, monitor CPU usage, reapply thermal paste, and place the computer in a cooler environment.
5. How can I prevent CPU overheating in the future?
Regularly clean your computer, monitor temperatures, replace thermal paste as needed, and ensure the system is in a cool, ventilated area with an upgraded cooling system if necessary.
Conclusion
CPU overheating happens when temperatures exceed safe limits, leading to slowdowns, crashes, or shutdowns. To prevent this, ensure proper airflow, clean the system regularly, and monitor CPU temperatures. Also, check the cooler, reapply thermal paste if needed, avoid overclocking, and place your system in a cool, well-ventilated environment to maintain optimal performance and prevent damage.