Cpu Bottleneck – What It Is And How To Fix It!
A CPU bottleneck occurs when the CPU can’t match the performance of other components like the GPU, causing slowdowns. Upgrade or optimize it.
This article explains the CPU bottleneck in simple words, using clear headings to guide you.
Table of Contents
What Is a CPU Bottleneck?
A CPU bottleneck happens when the processor cannot match the performance of other components, such as the GPU, slowing overall system efficiency. This occurs when the CPU processes data slower than required, causing delays in tasks like gaming. For instance, pairing a powerful GPU with an older or underperforming CPU can limit performance, as the CPU becomes the weakest link, reducing the system’s ability to operate at its full potential.
Signs of a CPU Bottleneck:
Here are some common signs that your CPU may be bottlenecking your system:
Low FPS in Games:
Low FPS in games, even with a high-performance GPU, indicates a CPU bottleneck. The processor cannot process game data fast enough, preventing the GPU from reaching its full potential. This results in choppy or sluggish gameplay, especially in CPU-intensive games. A mismatch between a powerful GPU and an older or weaker CPU often causes this issue, limiting overall gaming performance. Upgrading the CPU can resolve this problem and improve gaming experiences.
High CPU Usage:
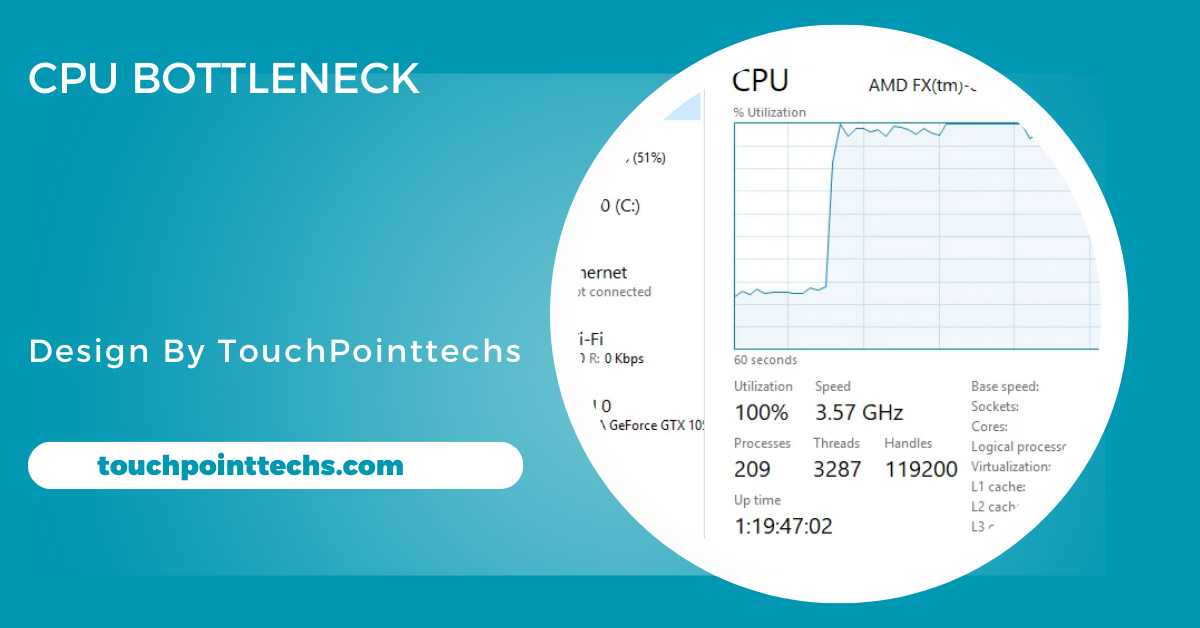
When CPU usage constantly reaches 90–100%, while GPU utilization remains low, a bottleneck is likely. The overworked processor struggles to keep up, creating imbalances and slowing overall system performance. Tasks like physics calculations or AI in games intensify this issue. The GPU ends up waiting for the CPU to finish its tasks, reducing efficiency. Addressing this mismatch by upgrading the CPU can significantly improve system balance and performance.
Slow Multitasking:
Lag or freezing during multitasking is a clear sign of a CPU bottleneck. Running multiple programs simultaneously overwhelms the processor, particularly in systems with limited cores or older CPUs. Basic tasks, like switching apps or opening files, become slow and inefficient. Even with adequate RAM and GPU resources, an overburdened CPU limits performance. Upgrading to a modern, multi-core processor can enhance multitasking and overall productivity significantly.
Delays in Rendering or Video Editing:
Delays in rendering or video editing often stem from an underpowered CPU. These tasks heavily depend on the processor for encoding, effects processing, and timeline scrubbing. Even with a robust GPU and sufficient RAM, an outdated CPU slows progress, increasing project completion times. This bottleneck interrupts workflows and reduces efficiency. Investing in a faster, multi-core CPU ensures smoother performance and quicker rendering or editing for professional and creative tasks.
How to Fix a CPU Bottleneck:
- Upgrade Your CPU: Upgrading to a more powerful CPU with more cores or a higher clock speed can alleviate the bottleneck. Choose a processor that matches the performance of your GPU to ensure balanced performance.
- Overclock Your CPU: If your CPU supports overclocking, consider increasing its clock speed for better performance. However, make sure you have proper cooling to prevent overheating.
- Optimize Background Processes: Close unnecessary programs running in the background to free up CPU resources. This will help improve overall performance by reducing the load on the processor.
- Improve Cooling: Overheating can throttle your CPU’s performance. Upgrade your cooling system with better fans, thermal paste, or even a liquid cooling system to keep the CPU running at optimal speeds.
- Upgrade Other Components: Sometimes, upgrading RAM or your storage device (e.g., using an SSD) can ease the load on your CPU, improving overall system performance and reducing bottlenecking.
By addressing the CPU bottleneck through these methods, you’ll be able to improve your system’s performance and avoid slowdowns.
Causes of CPU Bottleneck:
Mismatched Components:
A CPU bottleneck often arises from pairing mismatched components, such as a high-end GPU with an entry-level CPU. The processor becomes the weaker link, unable to handle data fast enough for the GPU, which limits overall performance. This imbalance prevents hardware from working at its full potential, leading to lag in games or demanding tasks. Ensuring balanced components during a PC build or upgrade can prevent such mismatches and improve system efficiency.
Outdated Processor:
An outdated CPU lacking modern features or multiple cores can struggle with current software or games. As technology advances, newer applications demand more processing power. Older processors may fail to handle these demands, leading to delays, stuttering, or multitasking inefficiencies. Even with sufficient RAM and a powerful GPU, a dated CPU becomes a bottleneck. Upgrading to a modern processor ensures smoother performance and compatibility with the latest applications.
Background Processes:
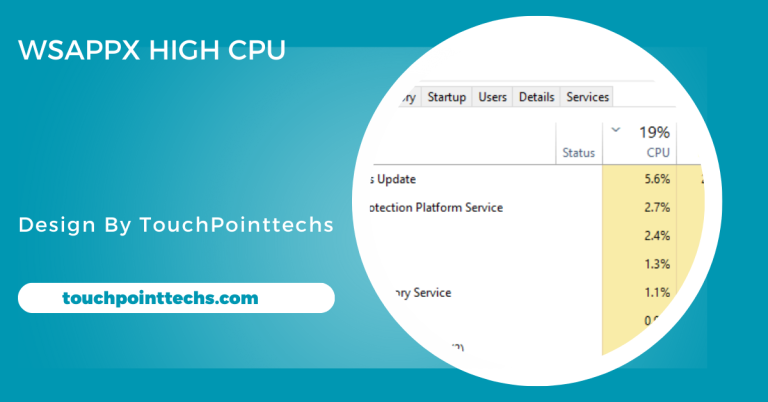
Too many background processes running simultaneously can overload the CPU and contribute to a bottleneck. Applications such as antivirus software, system updates, or unnecessary programs consume processing power, leaving less available for primary tasks. This results in reduced system responsiveness and performance. Regularly monitoring and managing background applications through the task manager can alleviate this issue, allowing the CPU to focus on essential tasks efficiently.
How to Check for a CPU Bottleneck:
Use Task Manager:
Launch Task Manager using Ctrl + Shift + Esc to observe system performance. Check the CPU and GPU usage during demanding tasks. If the CPU consistently operates at 90–100% while the GPU remains underused, this indicates a bottleneck. This simple tool provides an effective way to identify imbalances, especially during gaming or multitasking. Regular monitoring can also highlight areas for hardware upgrades to optimize overall system performance and reduce bottlenecks.
Benchmark Tools:
Use benchmarking software like MSI Afterburner or HWMonitor to analyze system performance. These tools provide real-time data on CPU and GPU usage, temperatures, and frame rates. If the CPU operates at full capacity while the GPU usage is low, it suggests a bottleneck. Benchmarking offers precise insights into how your hardware performs under stress, helping you identify which components need upgrading to achieve a more balanced and efficient setup.
Game Testing:
Lowering graphics settings in games can help identify a CPU bottleneck. If the FPS remains unchanged, even at reduced settings, the CPU may be struggling to process data fast enough. This simple method is especially useful for diagnosing performance issues without requiring specialized software. Consistent results across various games can confirm whether the CPU is the limiting factor, guiding you toward potential upgrades or system adjustments.
Is a 10% processor bottleneck bad?
A 10% processor bottleneck is generally not significant and typically won’t cause noticeable issues in most tasks. It means the CPU is being slightly slower than the GPU or other components, but the difference is minimal. However, if you’re experiencing performance drops, especially in demanding tasks like gaming or video editing, a 10% bottleneck may be worth addressing. It’s always best to monitor performance over time and consider an upgrade only if the bottleneck becomes more pronounced.
FAQ’S
1. What is a CPU bottleneck?
A CPU bottleneck occurs when the processor is slower than the GPU, limiting the system’s overall performance. It causes delays in tasks like gaming and multitasking.
2. How do I know if my CPU is bottlenecking?
Use Task Manager to check if the CPU usage is high (90-100%) while the GPU is underused. This indicates a bottleneck.
3. Can overclocking fix a CPU bottleneck?
Overclocking can improve CPU performance, but it requires good cooling to avoid overheating. It may help alleviate some bottleneck issues.
4. Is it bad to have a small bottleneck (10%)?
A 10% bottleneck generally doesn’t cause significant issues for most tasks. However, if it affects performance, consider addressing it.
5. How can I fix a CPU bottleneck?
You can fix it by upgrading your CPU, optimizing background processes, or improving system cooling to balance CPU and GPU performance.
Conclusion
A 10% processor bottleneck is typically minor and won’t cause noticeable problems for most tasks. It means the CPU is slightly slower than the GPU or other components. However, if performance issues arise in demanding tasks like gaming or video editing, it may be worth addressing. Monitor your system’s performance and consider upgrading if the bottleneck becomes more pronounced.