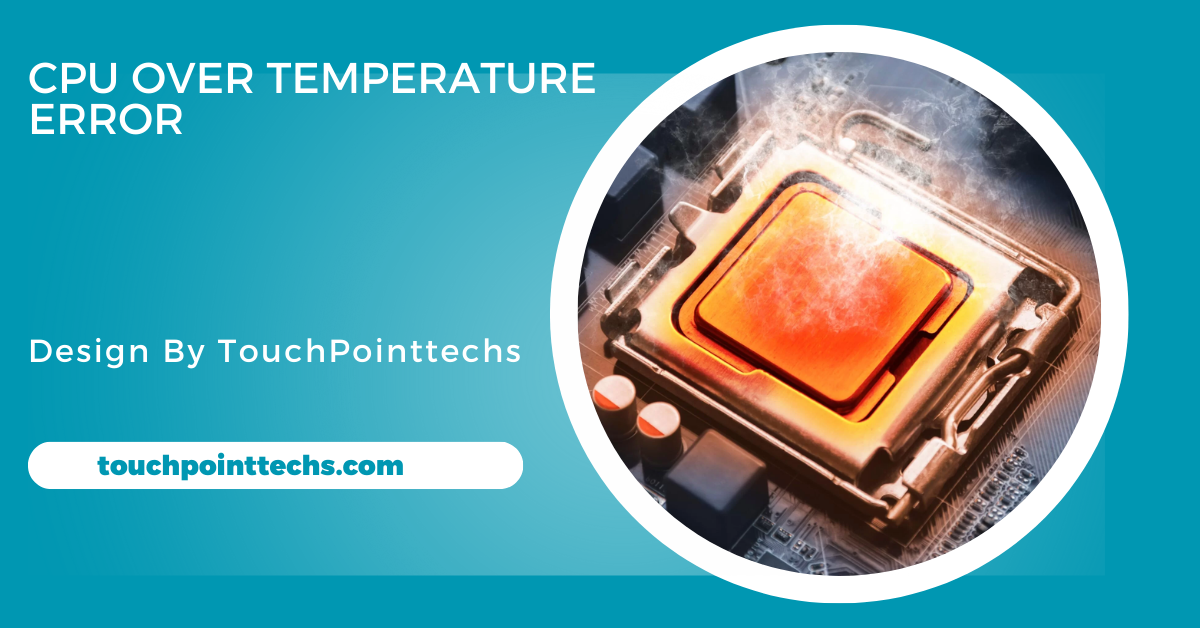
Cpu Over Temperature Error – Discover The Causes, Solutions, and Prevention!
A CPU Over Temperature Error can be alarming, especially for those unfamiliar with computer hardware. This error occurs when the processor exceeds its safe temperature limits, which can lead to performance issues, hardware damage, or system shutdowns. In this guide, we’ll explore the causes, solutions, and preventative measures to help you address and avoid this issue.
Table of Contents
What is a CPU Over Temperature Error?
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of your computer, performing billions of calculations every second. When a CPU overheats, the system triggers a warning or shuts down to prevent permanent damage. The CPU Over Temperature Error is often displayed during boot-up or while the system is running demanding tasks.
Common Causes of CPU Over Temperature Error
- Insufficient Cooling: Faulty or insufficient cooling systems, such as non-functional fans or clogged air vents, can prevent proper heat dissipation.
- Dust and Dirt Accumulation: Dust buildup on the heatsink, fan, or inside the computer case restricts airflow, causing overheating.
- High Workload or Overclocking: Running intensive applications or overclocking the CPU beyond its recommended limits can significantly raise its temperature.
- Old or Dried Thermal Paste: Thermal paste, which helps transfer heat from the CPU to the heatsink, loses effectiveness over time.
- Poor Case Ventilation: Lack of adequate airflow within the computer case can trap heat, especially in compact or poorly ventilated setups.
- Hardware Malfunction: Faulty cooling components, such as broken fans or defective temperature sensors, can lead to overheating.
How to Fix a CPU Over Temperature Error
1. Check and Clean the Cooling System
- Inspect Fans and Heatsinks: Ensure the CPU fan and heatsink are clean and operational.
- Remove Dust: Use compressed air to clean dust from the cooling components and air vents.
2. Reapply Thermal Paste
- Remove the old thermal paste using isopropyl alcohol.
- Apply a pea-sized amount of new, high-quality thermal paste to the CPU before reattaching the heatsink.
3. Optimize Case Ventilation
- Ensure your computer case has sufficient airflow by arranging cables neatly and adding additional case fans if necessary.
- Use a larger or better-ventilated case if overheating persists.
4. Check System Settings
- Disable Overclocking: If overclocking is enabled, revert to the default settings in your BIOS or motherboard software.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use software like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or SpeedFan to track CPU temperatures and fan speeds.
5. Upgrade Cooling Solutions
- Replace the stock cooler with a high-performance air or liquid cooling system for better thermal management.
- Consider upgrading to a larger heatsink or adding more case fans for enhanced cooling.
6. Update BIOS and Drivers
- Ensure your system’s BIOS and drivers are up to date, as updates often include optimizations for hardware performance.
Preventing CPU Over Temperature Errors
- Regular Maintenance: Clean your computer’s interior every 3–6 months to prevent dust buildup.
- Monitor CPU Temperatures: Use monitoring tools to keep track of CPU temperatures, especially during intensive tasks like gaming or rendering.
- Invest in Quality Components: Purchase reliable cooling solutions and use high-quality thermal paste for effective heat management.
- Avoid Overclocking: If you’re unfamiliar with overclocking, avoid pushing your CPU beyond its factory specifications.
- Ensure Proper Placement: Place your computer in a well-ventilated area, away from walls or other obstructions that could block airflow.
Signs of an Overheating CPU
- Frequent system crashes or blue screen errors.
- Sluggish performance during resource-intensive tasks.
- Loud fan noise as the system attempts to cool the CPU.
- Automatic shutdowns to prevent hardware damage.
FAQs About CPU Over Temperature Error
1. What is a safe operating temperature for a CPU?
Most CPUs operate safely between 40–70°C under normal conditions and up to 85°C under heavy loads.
2. Can I still use my computer after seeing a CPU Over Temperature Error?
You should address the issue immediately, as continued use could damage your CPU or motherboard.
3. What happens if my CPU overheats frequently?
Frequent overheating can lead to reduced performance, shortened hardware lifespan, or permanent damage.
4. How do I check my CPU temperature?
Use tools like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or your BIOS interface to check the temperature.
5. Does overclocking cause overheating?
Yes, overclocking increases the CPU’s power consumption and heat output, requiring advanced cooling.
6. When should I replace my CPU cooler?
Replace your CPU cooler if it’s damaged, inefficient, or unable to maintain safe temperatures under load.
7. Can dust alone cause a CPU Over Temperature Error?
Yes, dust buildup can block airflow, making it difficult for cooling systems to regulate temperature.
8. Is liquid cooling better than air cooling?
Liquid cooling offers superior heat dissipation, especially for high-performance CPUs or overclocked systems.
9. How often should I reapply thermal paste?
Reapply thermal paste every 2–3 years or whenever replacing the cooler.
10. Can an overheating CPU damage other components?
Yes, prolonged overheating can damage the motherboard, RAM, and other nearby components.
Conclusion
A CPU Over Temperature Error is a critical warning that should not be ignored. By identifying the causes and implementing the solutions outlined above, you can protect your system from damage and ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance, monitoring, and investing in quality cooling solutions will help you prevent this issue and keep your computer running smoothly.