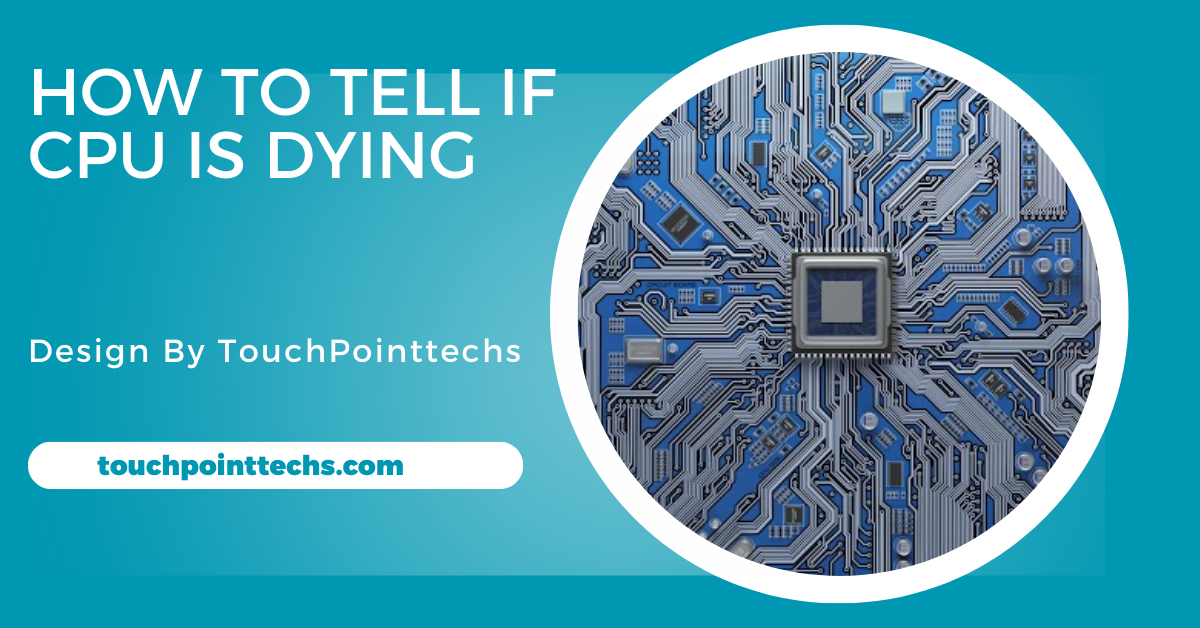
How To Tell If Cpu Is Dying – Tips And Tricks!
To determine if your CPU is failing, watch for frequent crashes, BSOD errors, overheating, slow performance, and random freezes for early detection.
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about identifying a failing CPU, reasons why it may happen, and how to test and prevent CPU issues.
Table of Contents
Why Is It Important to Know if Your CPU Is Dying?
A healthy CPU is crucial for your computer’s overall performance. A dying CPU can lead to frustrating issues like random shutdowns, errors, and complete system crashes. Early identification allows you to:
- Prevent System Failures: Avoid sudden crashes that disrupt your work or gaming.
- Protect Your Data: Reduce the risk of losing important files due to unexpected shutdowns.
- Save on Repair Costs: Replacing a failing CPU before it completely dies is often cheaper than dealing with additional damaged components.
Let’s look at the common signs that your CPU might be in trouble.
Common Signs That Your CPU Might Be Dying:
Frequent System Crashes:
Frequent system crashes and unexpected reboots during simple tasks can indicate a failing CPU. If your computer shuts down without warning, especially during routine operations, this could suggest a malfunctioning processor. Pay attention to these symptoms to prevent further damage and ensure your computer’s reliability.
Blue Screen of Death (BSOD):
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a strong indicator of hardware issues, including potential CPU failure. If you encounter BSOD errors frequently, especially during regular activities or resource-heavy applications, it’s essential to investigate. Document any error codes that appear, as they can help diagnose the problem and determine necessary actions.
Overheating Issues:
If your CPU overheats during light tasks, it’s a significant warning sign. Look for high temperature readings, constant fan operation, and excessive heat when touching the case. Overheating can lead to throttling, reducing performance, and could even cause the system to shut down to prevent further damage. Monitor temperatures regularly.
Poor Performance and Slowdowns:
Sudden performance drops, such as slow application launches and lag during normal operations, may suggest CPU issues. If your computer frequently freezes or responds slowly to commands, it’s crucial to investigate potential problems. These symptoms might worsen over time, making early detection important for maintaining optimal performance.
Random Freezes and Application Failures:
Random freezes and application crashes are common signs of a failing CPU. If your computer becomes unresponsive without warning or requires hard reboots to regain functionality, these issues could point to hardware problems. Monitor these occurrences closely, as they can signal underlying issues that need to be addressed promptly.
Why Does a CPU Fail?
Overheating:
Overheating is a major cause of CPU failure. When a CPU exceeds its optimal temperature, internal circuits can suffer damage. To prevent this, ensure adequate airflow within the computer case, regularly clean fans and vents of dust, and apply high-quality thermal paste between the CPU and heatsink for better heat transfer.
Power Surges:
Power surges pose a serious threat to CPU integrity. Sudden voltage spikes can destroy sensitive components inside the CPU, leading to irreversible damage. Protect your system by using a reliable surge protector to manage unexpected voltage changes. Additionally, consider investing in an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) to provide stable power during outages.
Physical Damage:
Physical damage is often a result of mishandling the CPU or its components during installation or maintenance. Accidental bumps or applying too much force can create micro-cracks or other damage. To avoid this, handle the CPU and motherboard gently, ensure components are securely mounted, and avoid excessive force to prevent socket damage.
Aging Hardware:
As with all technology, CPUs have a limited lifespan, typically lasting 7-10 years under normal use. Over time, internal parts can wear down, leading to decreased performance or total failure. To extend your CPU’s lifespan, maintain a clean environment, consider upgrading the cooling solution, and regularly monitor performance for early signs of deterioration.
What to Do if Your CPU Is Dying:
Once you’ve determined that your CPU may be failing, you can take steps to fix or limit the damage. Below are practical solutions to help address a dying CPU.
Clean the Cooling System:
Dust and dirt can block the airflow to your CPU, causing overheating. Clean the fans, heat sinks, and vents thoroughly. Use compressed air to remove dirt and ensure cables are neatly managed to avoid obstructing airflow. Proper airflow can significantly reduce heat buildup and prolong your CPU’s lifespan.
Replace the CPU Fan or Heat Sink:
If cleaning doesn’t reduce the CPU temperature, consider replacing the fan or upgrading the heat sink. Investing in a high-quality cooling system can help maintain optimal CPU temperatures, improving stability and performance. Upgrading the cooling solution can be particularly beneficial for intensive tasks like gaming or video editing.
Upgrade Your CPU:
If your CPU is outdated and performance issues persist, upgrading to a newer model might be necessary. Make sure the new CPU is compatible with your current motherboard. An upgraded CPU can provide better performance, energy efficiency, and support for newer technologies, giving your system a fresh boost.
Use a Surge Protector:
A quality surge protector can shield your computer from unexpected voltage spikes that can harm your CPU and other components. Surge protectors are affordable and easy to install. Investing in one can prevent power-related issues in the future, protecting your hardware from electrical damage.
Tips to Prevent CPU Failure:
Maintain Proper Cooling:
Ensure your CPU stays cool by keeping your cooling system clean and effective. Regularly clean dust from fans, heat sinks, and vents. Consider upgrading to a higher-quality fan or heatsink if needed. Proper airflow can prevent overheating and prolong the CPU’s life.
Use High-Quality Thermal Paste:
Apply a good-quality thermal paste between the CPU and heat sink. This paste helps transfer heat from the CPU to the cooler, reducing temperature. Replace the thermal paste every couple of years to maintain efficient heat dissipation and ensure the CPU runs smoothly.
Protect Against Power Surges:
Safeguard your CPU from sudden voltage spikes by using a reliable surge protector. If you experience frequent power outages or unstable electricity, consider investing in an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) to maintain consistent power and avoid potential damage to the CPU.
Avoid Overclocking Without Proper Cooling:
Overclocking can improve performance, but it increases the CPU’s temperature. Only overclock if you have an advanced cooling system in place. Monitor your CPU’s temperature regularly to ensure it stays within safe limits, especially when running demanding tasks.
Keep Your Computer Environment Clean and Ventilated:
Keep your PC in a cool, dust-free environment. Avoid placing it in direct sunlight or confined spaces that can trap heat. Ensure proper ventilation around your computer case, and avoid blocking vents with objects. A clean environment helps maintain stable temperatures and prevents hardware wear.
FAQ’s
1. What are common signs of a failing CPU?
Common signs include frequent system crashes, the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), overheating, poor performance, and random freezes.
2. How can I prevent CPU failure?
Prevent CPU failure by maintaining proper cooling, using high-quality thermal paste, protecting against power surges, avoiding overclocking without adequate cooling, and keeping your computer environment clean.
3. What causes CPU failure?
CPU failure can be caused by overheating, power surges, physical damage during installation, and aging hardware.
4. How can I check my CPU temperature?
You can check your CPU temperature using monitoring software like HWMonitor or Core Temp, which display real-time temperature readings.
5. Should I replace my CPU if it’s failing?
If your CPU shows signs of failure and cleaning or upgrading cooling does not help, replacing it may be necessary for better performance and system stability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the signs of a failing CPU is crucial for maintaining computer performance. Frequent crashes, overheating, and slowdowns indicate potential issues. Early detection allows you to take action, such as cleaning or upgrading components, which can prevent further damage and data loss. Staying vigilant ensures your system remains stable and efficient, prolonging its overall lifespan.