Wmi Provider Host High Cpu – What It Is And How To Fix It!
WMI Provider Host manages Windows system data. High CPU usage occurs due to issues like malware or corrupted repositories. Fixes include updates.
In this article, we’ll explain what WMI Provider Host is, why it uses a high CPU, and how you can fix it. We will also provide simple and practical solutions for this problem.
Table of Contents
What is a WMI Provider Host?
Definition of WMI Provider Host:
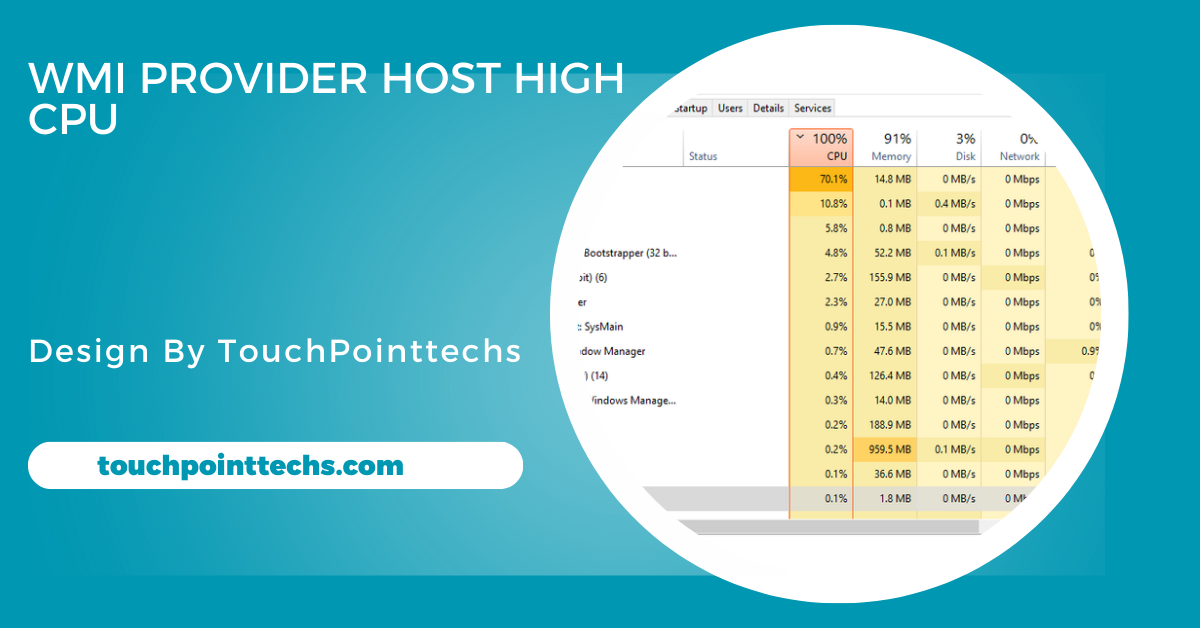
WMI stands for Windows Management Instrumentation, a system feature that allows monitoring and management of various aspects of your computer. The WMI Provider Host, or WmiPrvSE.exe, is a service that gathers information from both hardware and software components. This data is utilized by applications and services to perform essential tasks like system monitoring, diagnostics, and troubleshooting. It typically operates quietly in the background unless there’s a performance issue.
Why is WMI Provider Host Important?
The WMI Provider Host plays a crucial role in helping the operating system and other software interact with hardware components on your computer. It is instrumental for tools like Task Manager, Event Viewer, and system health monitors, which rely on this data to perform effectively. Without WMI, important system management tasks would not work properly, affecting diagnostics, resource monitoring, and troubleshooting processes.
Can I Close My WMI Provider Host?
No, you should not close the WMI Provider Host as it is an essential service for Windows. It allows various programs to gather data about your system for tasks like monitoring and diagnostics. Closing it can cause issues with system functionality, such as incorrect data display in Task Manager or errors in troubleshooting tools. If it uses excessive CPU, troubleshooting the cause is a better approach than closing it.
Is It Okay to Disable WMI?
Disabling the WMI Provider Host is not recommended because it is a critical Windows service. Many applications and system features rely on WMI to function correctly. Disabling it can lead to problems with system monitoring, hardware management, and even some software features. If WMI is causing high CPU usage, resolving the issue through proper fixes like restarting the service or scanning for malware is more effective.
What Causes High CPU Usage by WMI Provider Host?
Normal WMI Provider Host CPU Usage:
Under normal circumstances, WMI Provider Host uses minimal CPU and operates quietly in the background without affecting performance. However, at times, it may consume excessive CPU, slowing down the system. This increase in usage could be due to several factors, such as third-party applications requesting more data, a corrupted WMI repository, or system misconfigurations. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause can help restore normal CPU usage and improve performance.
- Third-Party Applications: Certain third-party applications using WMI to monitor your system may cause high CPU usage. These programs can overburden the CPU by requesting extensive data from WMI, leading to increased resource consumption.
- Corrupted WMI Repository: The WMI repository stores collected system data, and if it becomes corrupted, it can create problems. A corrupted repository may result in WMI Provider Host consuming excessive CPU as it struggles to access invalid information, which affects performance.
- Malicious Software or Malware: Malware or malicious software can sometimes disguise itself as WMI Provider Host, consuming CPU resources. If you notice high CPU usage with no apparent reason, it’s advisable to scan for potential malware infections to prevent performance degradation.
- Misconfigured System Settings: Incorrect or misconfigured system settings can also cause WMI Provider Host to use excessive CPU. Problems with event logs or faulty settings that trigger unnecessary data collection can lead to unnecessary resource usage, impacting overall performance.
How to Fix WMI Provider Host High CPU Usage:
Restart the WMI Service:
Press Windows + R, type services.msc, and press Enter. Locate the Windows Management Instrumentation service, right-click, and select Restart. Restarting clears any temporary issues causing high CPU usage. It resets the service, ensuring smooth operations. If this step doesn’t solve the issue, consider additional troubleshooting options. Regularly restarting services can prevent such problems from recurring and improve your system’s performance over time.
Check for Problematic Applications:
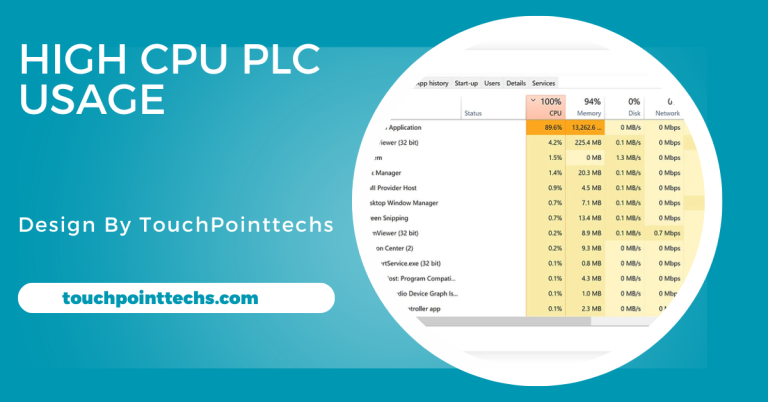
Open Task Manager using Ctrl + Shift + Esc and examine the processes tab. Look for applications using excessive CPUs linked to WMI. Close unnecessary programs and uninstall or update problematic software. Applications requesting frequent data from WMI can overload the service. By identifying and managing such software, you can significantly reduce CPU usage and improve your system’s responsiveness without affecting essential functions.
Scan for Malware or Viruses:
Run a full scan using Windows Defender or a trusted antivirus program. Malware often disguises itself as legitimate processes like WMI Provider Host, leading to high CPU usage. Detecting and removing these threats ensures your system remains secure. Regular malware scans also prevent resource-intensive activities that slow down your computer. Maintaining updated antivirus software is crucial for protecting your device from such issues in the future.
Rebuild the WMI Repository:
Open Command Prompt as Administrator by searching for “cmd” and selecting Run as Administrator. Type winmgmt /resetrepository and press Enter. Restart your system to rebuild the WMI repository. This process resolves corrupted repository issues causing high CPU usage. A fresh repository ensures the service functions correctly, reducing unnecessary resource consumption. Regular maintenance of system repositories helps in preventing such performance problems.
Update Windows System:
Navigate to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and click Check for updates. Download and install any pending updates. System updates often contain patches that address bugs causing high CPU usage by WMI. Keeping your Windows updated ensures compatibility with applications and enhances overall system stability. Regular updates also introduce security improvements that safeguard against vulnerabilities affecting performance.
Disable Unnecessary Services:
Access Services using services.msc, locate non-essential services linked to WMI, right-click, and choose Stop or Disable. Disabling unnecessary services reduces the workload on WMI, preventing high CPU usage. Be cautious to avoid stopping critical system services. This action optimizes resource allocation and enhances system performance by eliminating unneeded background processes. Always review the service’s purpose before disabling it.
Check Event Viewer for Errors:
Open the Event Viewer by pressing Windows + X and selecting it. Navigate to Windows Logs > Applications, and search for errors related to WMI. Analyze error details to identify problematic applications or configurations. Address recurring errors by fixing the source or reconfiguring settings. Monitoring event logs provides valuable insights into system issues and helps resolve CPU usage concerns effectively. Regular checks ensure proactive problem resolution.
Can I Close My WMI Provider Host?
No, you should not close the WMI Provider Host as it is an essential service for Windows. It allows various programs to gather data about your system for tasks like monitoring and diagnostics. Closing it can cause issues with system functionality, such as incorrect data display in Task Manager or errors in troubleshooting tools. If it uses excessive CPU, troubleshooting the cause is a better approach than closing it.
Is It Okay to Disable WMI?
Disabling the WMI Provider Host is not recommended because it is a critical Windows service. Many applications and system features rely on WMI to function correctly. Disabling it can lead to problems with system monitoring, hardware management, and even some software features. If WMI is causing high CPU usage, resolving the issue through proper fixes like restarting the service or scanning for malware is more effective.
What Is Causing 100% CPU Usage?
100% CPU usage can be caused by various factors, including:
- Background Applications: Resource-intensive apps running in the background.
- Malware or Viruses: Malicious programs overloading the CPU.
- Corrupted System Files: Damaged files affecting system performance.
- High Demands on WMI: Excessive requests from applications using the WMI service.
Resolving this involves identifying the root cause through Task Manager or Event Viewer, and taking steps like updating software, scanning for malware, or repairing system files.
FAQ’s
1. What is the WMI Provider Host?
The WMI Provider Host is a Windows service that collects and provides system information to applications for diagnostics and monitoring.
2. Why does the WMI Provider Host use a high CPU?
High CPU usage can occur due to issues like corrupted repositories, excessive requests from applications, or malware infections.
3. Can I disable the WMI Provider Host?
No, disabling it is not recommended as it is vital for Windows system functionality and monitoring processes.
4. How can I fix WMI Provider Host high CPU usage?
You can fix it by restarting the WMI service, scanning for malware, rebuilding the repository, or updating your system.
5. Is high CPU usage by WMI Provider Host harmful?
While it can slow down performance, it’s not harmful. Resolving the cause restores normal system functionality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the WMI Provider Host is a vital Windows service for system management and monitoring. High CPU usage often results from malware, corrupted repositories, or misconfigured settings. Effective fixes include restarting the WMI service, scanning for malware, rebuilding the repository, and updating Windows. Regular maintenance ensures smooth performance and prevents recurring issues, keeping your system running efficiently.