What Is A Cpu In A Car – The Role Of The Engine Control Unit!
A car’s CPU, called the Engine Control Unit (ECU), oversees engine performance, safety, and comfort features, ensuring efficient and safe vehicle operation.
In this article, we will explore what a CPU is in a car, its functions, types, and how it impacts your driving experience.
Table of Contents
What is a CPU?
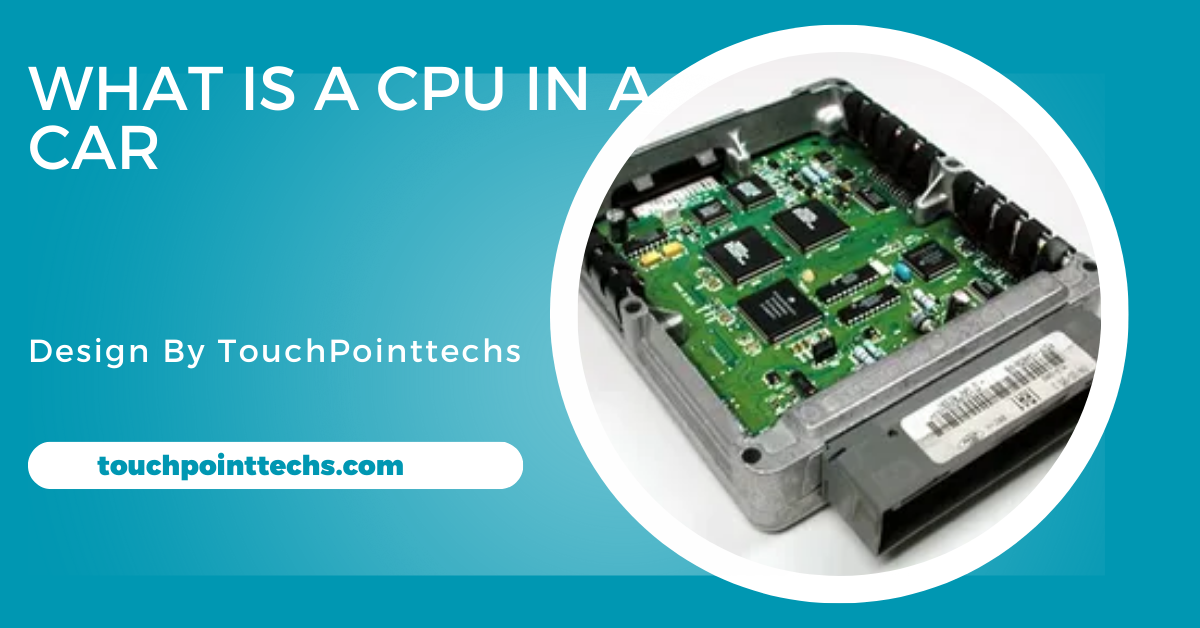
A Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of any device that uses electronics. In cars, a CPU controls the flow of information, making decisions based on data collected from various sensors. Modern vehicles are like computers on wheels, requiring CPUs to manage complex systems.
Definition of a CPU in a Car:
In cars, the CPU is often called the Engine Control Unit (ECU) or Electronic Control Module (ECM). It acts as the central brain, coordinating data and instructions to ensure the car runs smoothly. It monitors and controls everything from fuel injection to temperature, ensuring the engine and other systems work efficiently.
What Does a CPU Do in a Car?
The car’s CPU is responsible for a variety of tasks, each contributing to a smooth and safe driving experience.
Monitoring the Engine:
The car’s CPU monitors engine performance, adjusting the fuel-to-air ratio for efficient combustion. It regulates fuel injection and timing based on current driving conditions, optimizing performance while reducing emissions. This real-time monitoring ensures the engine operates smoothly, providing power when needed and conserving fuel when possible.
Controlling Safety Features:
The CPU manages safety systems like airbags, ABS, and stability control. It processes sensor data and determines when to activate these features. In a collision, for example, it deploys airbags to protect passengers. This quick response helps in maintaining control during emergency situations, enhancing the overall safety of the vehicle.
Managing Comfort Systems:
The CPU controls comfort features, such as climate settings, power windows, and seat adjustments. It processes driver inputs, making adjustments for a more pleasant driving experience. For example, it can regulate cabin temperature or adjust seat positions for comfort, ensuring that the car’s environment meets the driver’s preferences.
Types of CPUs in Cars:
There are different CPUs in cars, each handling specific tasks. Here’s a breakdown of the main types:
Engine Control Unit (ECU):
The ECU is the car’s primary CPU, managing engine functions like fuel injection, air intake, and exhaust emissions. It constantly adjusts these settings to optimize performance and fuel efficiency. By monitoring engine sensors, the ECU ensures the engine runs smoothly, providing power when needed and minimizing environmental impact.
Transmission Control Unit (TCU):
The TCU oversees the car’s transmission system, managing gear shifts based on driving conditions, speed, and engine load. It selects the appropriate gear for optimal performance and fuel efficiency, ensuring smooth acceleration and deceleration. This CPU plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable driving experience, especially in automatic transmissions.
Body Control Module (BCM):
The BCM manages the car’s electronic systems, including lights, windows, wipers, and locks. It communicates with sensors throughout the car to control and coordinate these functions. The BCM ensures the car’s electrical components work correctly, providing data to other CPUs for more integrated vehicle management.
Safety Control Unit (SCU):
The SCU is dedicated to safety systems, handling features like airbags, anti-lock brakes, and seat belt tensioners. It responds to sensor data, making split-second decisions to activate safety measures in emergencies. This CPU is crucial for maintaining passenger safety by quickly detecting and reacting to potential hazards.
Infotainment System CPU:
The Infotainment System CPU manages multimedia and navigation functions. It connects to the car’s GPS, audio systems, and other devices, offering drivers access to music, navigation, and communication. This CPU enhances the driving experience by delivering entertainment and essential information through the car’s display and control interface.
How Does a Car’s CPU Work?
A car’s CPU operates by receiving data from sensors throughout the vehicle. These sensors monitor various factors like speed and temperature. The CPU processes this information and then sends commands to different car systems, ensuring optimal performance and safety by adjusting operations like fuel injection, cooling, and air conditioning.
Data Collection:
Sensors in the car gather critical information, such as engine temperature, fuel levels, and wheel speed. This data is sent to the CPU for analysis. The accurate and constant collection of this information is crucial for the CPU to make precise adjustments and ensure the car functions smoothly.
Data Processing:
The CPU analyzes the collected data to make real-time adjustments. For instance, if the engine’s temperature rises, the CPU will activate the cooling system to prevent overheating. This processing ensures that the car operates efficiently and safely by responding dynamically to changes in the driving environment.
Command Execution:
After processing data, the CPU issues commands to different car systems, like adjusting fuel injection, tweaking the air conditioning, or activating safety features. This step ensures the vehicle’s components work in harmony, maintaining performance, comfort, and safety during the drive.
Signs of a Faulty Car CPU:
A malfunctioning car CPU can lead to multiple issues, impacting performance and safety. Problems can arise if the CPU fails to process or execute commands correctly, leading to erratic behavior in car systems. Monitoring symptoms can help diagnose potential CPU problems early.
Check Engine Light:
The Check Engine Light may illuminate due to a malfunctioning CPU. This warning light alerts the driver to issues detected within the car’s systems. A faulty CPU can trigger this light, indicating that further inspection and diagnostic work are needed to pinpoint the exact problem.
Engine Stalling or Misfiring:
Engine stalling or misfiring can result from a faulty CPU sending incorrect data to the engine. This leads to unpredictable behavior and poor performance, impacting the car’s drivability. If the problem persists, professional inspection is essential to assess the CPU’s condition.
Poor Fuel Efficiency
A drop in fuel efficiency may be linked to a problematic CPU. The CPU plays a key role in optimizing fuel consumption. When it malfunctions, the car may burn more fuel than necessary, increasing costs and reducing overall performance. This sign often requires diagnostic testing.
Difficulty Starting the Car:
Issues with starting the car can indicate a faulty CPU. If the CPU can’t manage the engine’s components properly, it can disrupt the startup process. This may result in delayed or failed engine starts, suggesting the need for a thorough examination of the CPU and related systems.
Can a Car Run Without a CPU?
No, modern cars rely heavily on CPUs to function. The CPU controls critical systems like the engine, transmission, and safety features. Without it, the car would not be able to run efficiently or safely. Older cars, built before electronics became standard, didn’t use CPUs, but modern vehicles are designed with CPUs at their core.
How to Maintain a Car’s CPU:
Regular Diagnostic Checks:
Get regular diagnostic checks for your car. Mechanics use special tools to connect with the car’s CPU, allowing them to spot potential problems early. Regular diagnostics help maintain the CPU’s performance, ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly and avoiding costly repairs from unnoticed issues.
Keep Sensors Clean:
Keep the car’s sensors clean and in good working order. Dirty or malfunctioning sensors can send incorrect data to the CPU, leading to performance issues. Regular cleaning and inspections ensure accurate data flow, allowing the CPU to make precise adjustments and maintain the car’s optimal operation.
Avoid Electrical Overloads:
Avoid overloading the car’s electrical system with too many devices. Installing aftermarket electronics without proper wiring can strain the CPU, potentially causing damage. Always follow professional guidelines when adding electronic accessories to ensure the car’s CPU and electrical systems remain unaffected.
Update the Car’s Software:
Some modern cars allow CPU software updates to fix bugs, boost efficiency, or add features. Check with your car’s manufacturer or dealership for any available updates. Keeping the software current ensures the CPU runs optimally, improving overall vehicle performance and reliability.
FAQ’s
1. What is a CPU in a car?
A CPU in a car, commonly called the ECU, is the main computer that manages and controls vehicle functions like fuel injection, safety, and comfort features.
2. How does a car’s CPU affect driving performance?
The CPU optimizes engine performance, adjusts fuel efficiency, and controls gear shifts, making the car run smoothly and improving fuel economy.
3. What are the different types of CPUs in cars?
Cars have several types of CPUs, including the ECU for the engine, TCU for transmission, BCM for body controls, and SCU for safety features.
4. What happens if a car’s CPU is faulty?
A faulty CPU can lead to engine misfires, poor fuel efficiency, or problems starting the car, often triggering the Check Engine Light.
5. Can a modern car function without a CPU?
No, modern cars rely on CPUs to control essential systems like the engine and safety features, so they cannot run without one.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a car’s CPU, mainly the Engine Control Unit (ECU), is vital for regulating engine performance, safety features, and comfort systems. It processes data from various sensors to ensure optimal vehicle operation, enhancing fuel efficiency and safety. Regular maintenance and diagnostics are essential for keeping the CPU functioning correctly, thereby improving the overall driving experience and vehicle reliability.