Average Cpu Temp – What You Need To Know!
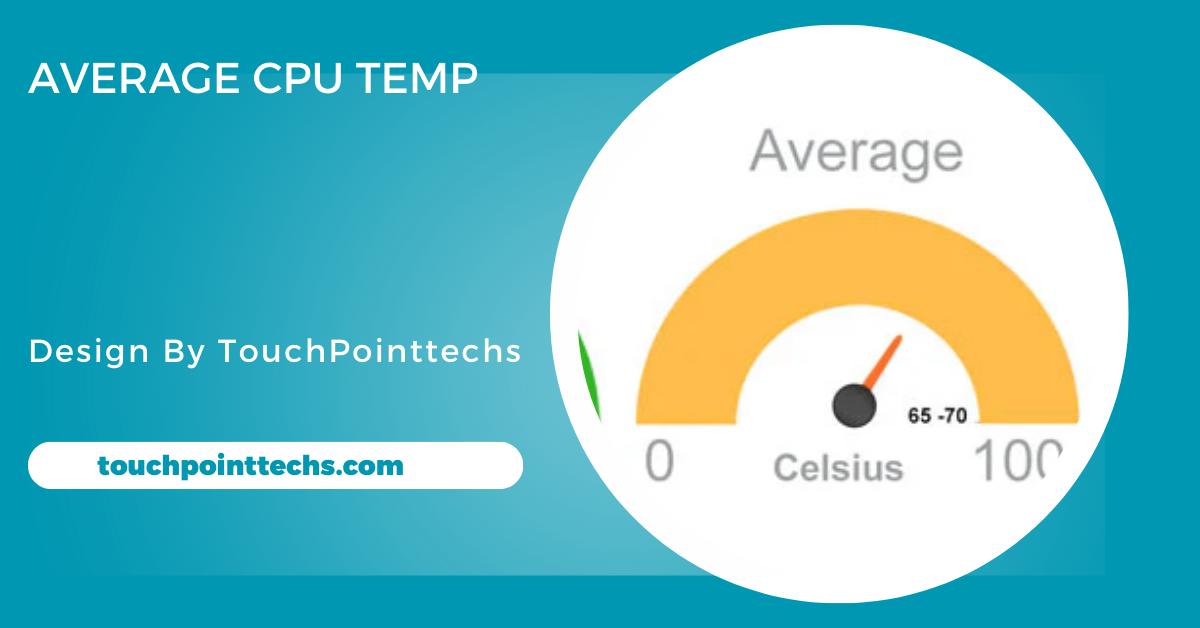
The average CPU temperature ranges from 30°C-50°C when idle and 60°C-85°C under load. Temperatures above 90°C are critical and can cause damage.
In this article, we will explain what is considered a normal temperature for your CPU, why it matters, and how to keep it at optimal levels.
Table of Contents
What Is CPU Temperature?
How the CPU Generates Heat:
The CPU generates heat as it processes tasks and performs calculations. The more demanding the tasks, the more heat it produces. Excessive heat can cause slow performance, system crashes, or even permanent damage. Monitoring the CPU temperature is crucial to ensure proper functioning and avoid overheating. Keeping the temperature within safe limits helps maintain system stability and prevents potential harm to the processor, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
What is Considered a Normal CPU Temperature?
The average CPU temperature can vary depending on factors like the type of processor, the workload on your computer, and the cooling system in place. However, there are general temperature ranges that you can keep in mind.
- Idle Temperature: When the computer is not doing heavy tasks (idle), the CPU temperature should typically be between 30°C and 50°C (86°F to 122°F).
- Load Temperature: When your computer is running demanding programs, such as video editing software or video games, the CPU temperature can rise. Under heavy load, a CPU temperature between 60°C and 85°C (140°F to 185°F) is normal.
- Critical Temperature: Anything above 90°C (194°F) is considered very high. Prolonged temperatures at this level can damage your CPU, and you should take steps to cool it down immediately.
Why Does CPU Temperature Matter?
Preventing Overheating:
Maintaining the CPU temperature within safe limits is crucial to avoid overheating, which can result in system slowdowns, instability, or even crashes. When the CPU gets too hot, it may throttle its performance to cool down, reducing processing power. Overheating over time can lead to permanent damage to internal components, affecting the overall lifespan and performance of your computer. Regular monitoring and cooling systems are essential to prevent overheating and ensure the CPU operates efficiently under load.
Protecting Your Investment:
Your computer and its components represent a valuable investment, and managing CPU temperature helps protect that investment. Overheating can lead to serious issues such as reduced performance, permanent damage, or even complete system failure. By actively monitoring and managing the temperature, you avoid expensive repairs or replacements due to overheating. Regularly ensuring the CPU remains within safe operating temperatures helps extend the life of your computer, saving money in the long run.
Improving Longevity:
Keeping your CPU temperature within a safe range is essential to improve the longevity of your computer. Much like how a car engine performs better and lasts longer with regular cooling, a CPU that stays within optimal temperatures works efficiently over time. Consistent overheating can degrade the components and shorten the lifespan of your system, leading to early malfunctions. A well-maintained cooling system and temperature management can significantly improve your computer’s durability and overall performance.
How to Monitor Your CPU Temperature:
Using Built-in Tools:
Many computers have built-in software to monitor the CPU temperature. On Windows PCs, you can check the temperature in the BIOS/UEFI settings. This allows you to see real-time data about your system’s performance. On Macs, however, you may need to install third-party apps to track CPU temperature, as macOS doesn’t offer built-in monitoring. These tools help ensure the CPU operates within safe temperature ranges.
Third-Party Software:
There are also many third-party programs that make it easy to track your CPU temperature in real-time. Some popular options include:
- Core Temp: A lightweight program that shows the temperature of each core in your CPU.
- HWMonitor: This program provides detailed information on the temperature, fan speed, and voltage of your computer.
- SpeedFan: A software that allows you to monitor your system’s temperature and adjust fan speeds.
These tools help you understand whether your CPU temperature is within safe levels or if action is needed.
Factors That Affect CPU Temperature:
The Type of CPU:
Different CPUs have specific temperature ranges. High-performance processors, like those in gaming computers, tend to generate more heat and run hotter than energy-efficient processors. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications to check your CPU’s recommended temperature range. Staying within this range is vital for optimal performance and to prevent damage over time, ensuring your computer functions smoothly without overheating or malfunctioning.
Ambient Temperature:
The temperature of the room where your computer is located affects the CPU’s temperature. A cooler room helps maintain a lower CPU temperature, whereas a warm room forces the CPU to work harder to maintain its cool, causing higher temperatures. Managing ambient temperature through proper ventilation or air conditioning can improve the performance and lifespan of your system by reducing the risk of overheating.
The Computer’s Cooling System:
A computer’s cooling system, including fans or liquid cooling, plays a vital role in maintaining a safe CPU temperature. If the cooling system is old, dirty, or insufficient, it may not perform efficiently, leading to overheating. Regular maintenance of cooling components and upgrading to more powerful cooling solutions can prevent this issue, ensuring the CPU runs at an optimal temperature and the system remains stable during intensive tasks.
Dust and Dirt:
Dust accumulation inside your computer can block airflow, preventing the cooling system from working efficiently. Dust buildup on fans, vents, or heat sinks can restrict airflow and lead to higher CPU temperatures. To prevent overheating, it’s important to clean the inside of your computer regularly. This will ensure that the cooling system operates effectively, maintaining an optimal temperature for the CPU and avoiding performance drops or damage.
Overclocking:
Overclocking increases your CPU’s clock speed, boosting performance but also generating more heat. This added heat requires a stronger cooling solution to keep the CPU temperature under control. If the cooling system is inadequate or the overclocking is too extreme, the CPU may overheat, leading to potential instability or damage. Properly balancing overclocking settings and maintaining a robust cooling system are essential to ensure safe and efficient operation.
FAQ’s
1. What is the normal CPU temperature for a computer?
The normal CPU temperature ranges from 30°C to 50°C when idle and between 60°C and 85°C under load.
2. How can I monitor my CPU temperature?
You can monitor your CPU temperature using built-in BIOS/UEFI settings or third-party software like Core Temp, HWMonitor, or SpeedFan.
3. What happens if the CPU temperature is too high?
High CPU temperatures can lead to slow performance, system crashes, or permanent damage to the processor.
4. Does the cooling system affect CPU temperature?
Yes, an efficient cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal CPU temperature. Insufficient or old cooling systems can cause overheating.
5. Can overclocking affect CPU temperature?
Yes, overclocking increases CPU heat output, and requires better cooling to prevent overheating and damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, keeping your CPU temperature within safe ranges is essential for maintaining system stability, preventing overheating, and extending the lifespan of your computer. Regular monitoring, efficient cooling, and cleaning are key to ensuring optimal performance. Managing temperature effectively helps avoid damage to components, protects your investment, and reduces the risk of costly repairs or system failures.